Underfloor heating is a form of heating in which the floor surface of a space is heated and this heat is then radiated throughout the space to create comfortable thermal conditions. It has been used for thousands of years as a form of space heating, most notably by the Romans, whose hypocaust system consisted of a raised floor through which warm air and smoke were drawn to heat the floor before being discharged through flues.
Modern underfloor heating tends to use either electrical resistance elements or fluid-flowing, hydronic systems to heat the floor.
Underfloor heating systems tend to be low-temperature systems, as the heating surface covers a much larger area than conventional radiators which because of their relatively small size have to operate at a high temperature.
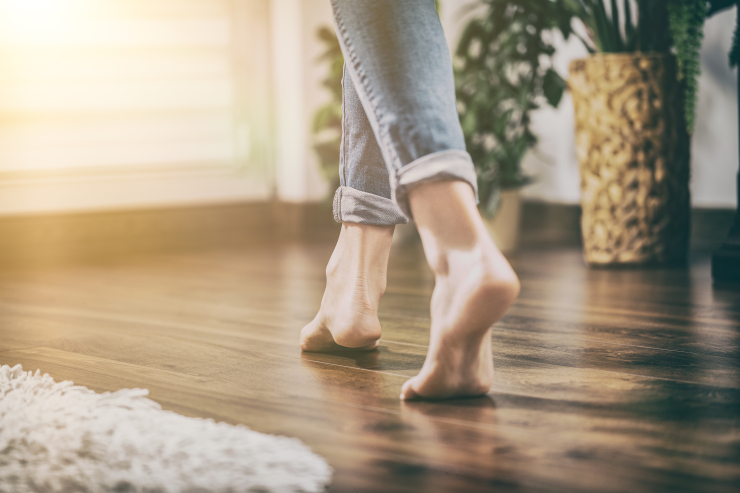

Underfloor heating can be installed on new-build projects, or retrofitted into existing spaces. It can be installed as the primary heating system or used to provide additional, localised heating in specific spaces such as bathrooms. It may be used in combination with renewable heat sources, thermal mass and night-time purging.
Systems can be modular or custom designed and installed, and will generally include insulation under the heat source to reduce heat loss.
Electric underfloor heating systems can sit beneath stone, tile, wood or even carpeted surfaces. A series of electric wires installed beneath or within the floor finish provide the heating element. There are a number of product types available, including loose-fit wiring, modular systems and heating mats.
The design of the installation will depend on the space size and dimensions, how well insulated it is, the nature of the flooring structure and the type of flooring covering. Generally, on new-build projects, cables or electric heating sheets are fitted beneath the floor finish on a layer of screed and insulation which ensure the floor is level and that the heat travels upwards into the space
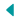
A fluid flowing hydronic system generally consists of a series of looped pipes connected to a boiler that circulate warm water through the floor. This needs enough space for the installation of piping and insulation and so floor levels may need to be elevated which can be difficult when retrofitting, increasing costs and disruption. For this reason they tend be better suited to new-build projects.
They can be more expensive to install than electrical systems, but may be less expensive to operate.
Because they are low temperature systems, they can easily incorporate renewable energy sources such as solar thermal panels, ground source heat pumps, air source heat pumps and so on.